📌What is a Database
What is a Database: A database is a structured collection of data that allows users to store, retrieve, manage, and manipulate information efficiently. It plays a crucial role in modern applications by supporting data-driven decision-making.
📌 Introduction to Database
What is a Database: Data refers to raw facts and figures related to an entity or object. Examples of data include names, ages, images, documents, and numbers.
📌Database
What is a Database: A database is an organized system that enables electronic storage and retrieval of data. Businesses and organizations use databases to manage customer records, financial transactions, employee details, and much more.
📌Real-World Database Examples
What is a Database
- Social Media (e.g., Facebook, Twitter) – Stores user profiles, posts, comments, and advertisements.
- Online Shopping Platforms (e.g., Amazon, eBay) – Manages product catalogs, customer details, and order processing.
- Banking Systems – Handles account details, transactions, and financial records.
- Healthcare Systems – Stores patient records, prescriptions, and medical history.
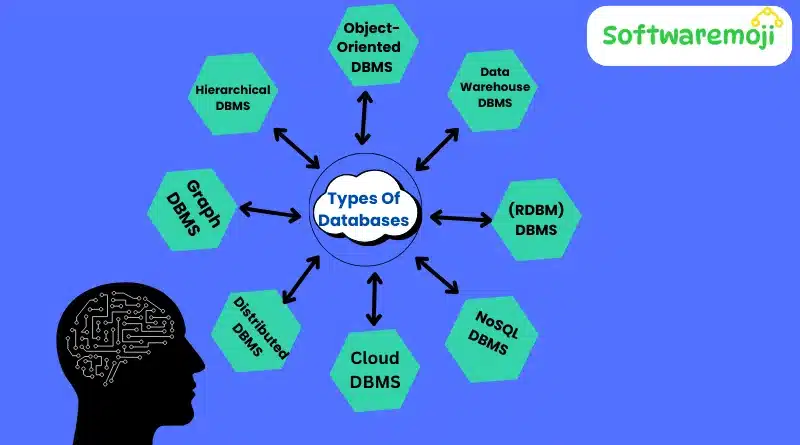
📌Types of Databases & Examples
1. Relational Database (RDBMS)
- Uses structured tables to store data.
- Examples: MySQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server.
2. NoSQL Database
- Used for handling large sets of unstructured data.
- Examples: MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis.
3. Cloud Database
- Hosted on cloud environments for scalability and accessibility.
- Examples: Google Cloud Firestore, Amazon RDS, Microsoft Azure SQL.
4. Distributed Database
- Stores data across multiple locations or servers.
- Examples: Apache Cassandra, Amazon DynamoDB.
5. Graph Database
- Uses graph structures to analyze relationships.
- Examples: Neo4j, ArangoDB.
6. Hierarchical Database
- Stores data in a tree-like structure.
- Example: IBM Information Management System (IMS).
7. Object-Oriented Database
- Stores data in objects similar to object-oriented programming.
- Example: PostgreSQL.
8. Data Warehouse
- Stores historical data for business intelligence and reporting.
- Examples: Amazon Redshift, Snowflake.
📌Key Components of a Database
- Hardware – Servers, storage devices, and networking components.
- Software – Database Management Systems (DBMS) like MySQL, Oracle.
- Data – Raw information stored within the database.
- Procedures – Guidelines and methods for managing databases.
- Database Access Language – SQL, NoSQL for querying and managing data.
📌 Database Management System (DBMS)?
What is a Database: A DBMS is software that allows users to create, manage, and manipulate databases efficiently.
Popular DBMS Software
- MySQL – Open-source RDBMS.
- Oracle Database – Enterprise-level DBMS.
- MongoDB – NoSQL database for big data applications.
- Microsoft SQL Server – Used for enterprise solutions.
📌Advantages of Using a Database
✅ Efficient data storage & retrieval
✅ Supports multiple applications & users
✅ Ensures data integrity and security
✅ Reduces redundancy and improves consistency
✅ Enables data analysis & reporting
📌Disadvantages of Databases
❌ High initial cost for setup & maintenance
❌ Requires skilled database administrators
❌ Risk of data loss due to hardware failures
❌ Performance issues with complex queries
Click To Open
👉Tutorial-2: MySQL Workbench Tutorial
👉Tutorial-3: SQL Tutorial for Beginners
