👉Object Repository in Selenium WebDriver
Object Repository in Selenium: In Selenium automation, maintaining web element locators in a centralized and modular way is crucial for scalability and maintainability. This is where an Object Repository comes into play.
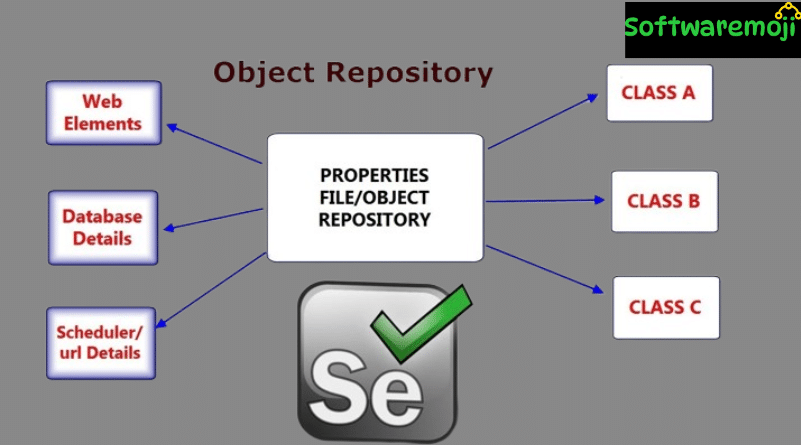
👉 What is an Object Repository?
Object Repository in Selenium: An Object Repository is a centralized storage location for all web element locators used in automation scripts. In the context of Selenium WebDriver, it helps manage elements separately from the test logic.
Benefits of Using Object Repository:
- Centralized management of locators
- Easier maintenance when locators change
- Enhanced framework modularity
- Reduced redundancy in test scripts
👉Types of Object Repositories in Selenium
Object Repository in Selenium: Although Selenium WebDriver doesn’t provide a built-in object repository, you can build one using external files.
🔸 Two Common Types:
- Properties File (Key-Value Pairs)
- XML File (Structured Tags Using DOM)
👉Object Repository Using Properties File
Object Repository in Selenium: A Properties file is a simple text file that stores data as key-value pairs. The key acts as the logical name for an object, and the value contains the locator to identify it on the web page.
✅ Step 1: Create a Properties File in Eclipse
- Right-click on your project → New → Other
- Select General > File and click Next
- Name the file with .properties extension (e.g., application.properties)
- The file will be added to your project structure
✅ Step 2: Storing Data in the Properties File
Open the application.properties file and add key-value pairs like:
properties
mobileTesting = //a[text()=’Mobile Testing’]
email = id:email
signUp = id:enterimg
Each key uniquely represents an element, and the value is its locator (XPath, ID, etc.)
✅ Step 3: Reading Data from Properties File
To read this data in your test scripts:
java
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(“path_to_file\\application.properties”);
prop.load(fis);
String mobileXPath = prop.getProperty(“mobileTesting”);
Use mobileXPath in your Selenium code like:
java
driver.findElement(By.xpath(mobileXPath)).click();
✅ Step 4: Using Properties File in Test Scripts
Your full test flow may look like this:
java
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(“path\\to\\application.properties”);
prop.load(fis);
driver.get(“https://demo.testsite.com”);
driver.findElement(By.xpath(prop.getProperty(“mobileTesting”))).click();
driver.navigate().back();
driver.findElement(By.id(prop.getProperty(“email”))).sendKeys(“test@example.com”);
driver.findElement(By.id(prop.getProperty(“signUp”))).click();
👉 Object Repository Using XML File
Object Repository in Selenium: An XML File (Extensible Markup Language) is a structured format similar to HTML that stores locators using a tag-based hierarchy. This method is more descriptive and supports nested data.
✅ Step 1: Create an XML File in Eclipse
- Right-click project → New → Other
- Select XML File under the XML folder → Click Next
- Enter a name like properties.xml → Click Finish
✅ Step 2: Store Data in XML Format
Example properties.xml content:
xml
<objects>
<mobileTesting>//a[text()=’Mobile Testing’]</mobileTesting>
<email>id:email</email>
<signUp>id:enterimg</signUp>
</objects>
✅ Step 3: Read Data from XML File
Use Java’s dom4j and jaxen libraries to parse XML. Add these JARs to your build path:
- dom4j-1.6.jar
- jaxen.jar
Sample code:
java
File inputFile = new File(“path_to_file\\properties.xml”);
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(inputFile);
String mobileXPath = doc.selectSingleNode(“//objects/mobileTesting”).getText();
👉 Step 4: Using XML Data in Test Scripts
java
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(“https://demo.testsite.com”);
String mobileXPath = doc.selectSingleNode(“//objects/mobileTesting”).getText();
driver.findElement(By.xpath(mobileXPath)).click();
String emailId = doc.selectSingleNode(“//objects/email”).getText();
driver.findElement(By.id(emailId)).sendKeys(“test@example.com”);
String signUpId = doc.selectSingleNode(“//objects/signUp”).getText();
driver.findElement(By.id(signUpId)).click();
👉 Summary
| Feature | Properties File | XML File |
| Format | Key-Value pairs | Tag-based structure (DOM) |
| Ease of Use | Simple and lightweight | Slightly more complex |
| Readable | Less descriptive | Human-readable and structured |
| Java Support | Built-in Properties class | Requires dom4j, jaxen libs |
| Use in Frameworks | Common in small-scale setups | Preferred in modular frameworks |
👉Key Takeaways:
- Object Repository in Selenium: An Object Repository helps you maintain locators outside test scripts.
- Properties files are simple to use and ideal for small-scale projects.
- XML files provide structure and scalability for large frameworks.
- Both can be easily integrated into Selenium WebDriver using Java.
