👉What is ER Modeling?
ER Modeling in DBMS: Entity-Relationship (ER) Modeling is a high-level data modeling technique used to define the structure of a database visually. It represents entities (objects), their attributes (properties), and relationships (connections) between them in a graphical format.
Why Use ER Modeling?
✅ Helps in database design by visually structuring data
✅ Serves as a non-technical communication tool between developers and stakeholders
✅ Identifies relationships between entities, ensuring efficient database structure
✅ Simplifies conversion to relational database schemas
👉Key Concepts in ER Modeling
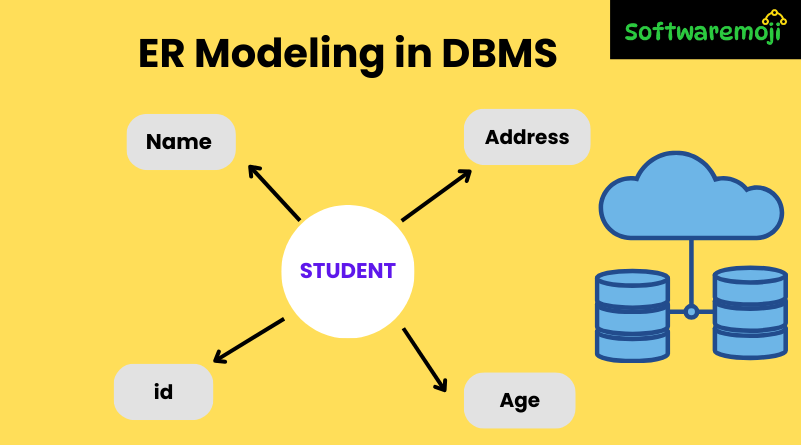
1. Entities
ER Modeling in DBMS: An entity is a real-world object or thing that can be uniquely identified.
🔹 Example: An “Employee” in a company is an entity.
Characteristics of Entities:
- Each entity has unique properties (attributes)
- Attributes can have single or multiple values
- Entities are distinguishable from each other
Example:
A Programmer working at Microsoft can have the following attributes:
| Attribute | Value |
| Name | Peter |
| Age | 30 |
| Department | IT |
2. Attributes
ER Modeling in DBMS: Attributes define properties of an entity.
🔹 Example: An Employee entity may have Name, Age, and Department as attributes.
Types of Attributes:
✅ ER Modeling in DBMS: Simple Attribute – Cannot be divided further (e.g., Age, Name)
✅ Composite Attribute – Can be divided into sub-parts (e.g., Full Name → First Name, Last Name)
✅ Derived Attribute – Can be computed from other attributes (e.g., Age derived from Date of Birth)
✅ Multivalued Attribute – Can have multiple values (e.g., Phone Numbers)
Example of Multivalued Attribute:
| Employee ID | Name | Phone Numbers |
| 101 | John | 9876543210, 8765432109 |
3. Relationships in ER Modeling
ER Modeling in DBMS: Entities interact with each other through relationships.
Example: If each employee is assigned a computer, then both Employee and Computer are entities, and their association is a relationship.
Types of Relationships in DBMS
1️⃣ One-to-One (1:1) – One entity is associated with only one other entity.
🔹 Example: A passport is assigned to only one person.
2️⃣ One-to-Many (1:M) – One entity is related to multiple entities.
🔹 Example: A teacher can teach multiple students.
3️⃣ Many-to-Many (M:N) – Multiple entities are related to multiple entities.
🔹 Example: A student can enroll in multiple courses, and each course can have multiple students.
👉Enhanced ER Model (EER)
ER Modeling in DBMS: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model is an advanced version of ER Modeling that supports more complex relationships and inherits features from object-oriented models.
Features of EER Model:
✅ Specialization – Creating sub-entities from a parent entity (e.g., Employee → Programmer, Manager)
✅ Generalization – Merging multiple entities into one (e.g., Car and Bike into Vehicle)
✅ Aggregation – A relationship between relationships
Example of Specialization:
General Entity: Employee
- Sub-Entities: Manager, Developer, Analyst
👉Case Study: ER Diagram for “MyFlix” Video Library
ER Modeling in DBMS: Let’s design an ER diagram for MyFlix Video Library, which rents out movies to members.
Step 1: Identify Entities
The main entities in MyFlix are:
📌 Members – Stores member details
📌 Movies – Stores movie details
📌 Categories – Stores movie genres (e.g., Action, Drama)
📌 Movie Rentals – Tracks which movies are rented out
📌 Payments – Stores payment details of members
Step 2: Define Relationships Between Entities
ER Modeling in DBMS: Solution for Many-to-Many Relationship:
Since relational databases do not support many-to-many relationships, we introduce an intermediate table called MovieRentals that connects Members and Movies.
👉Creating an ER Model in MySQL Workbench
Steps to Create an ER Diagram in MySQL Workbench
1️⃣ Open MySQL Workbench
2️⃣ Click on “+” (Add Diagram)
3️⃣ Double-click Add Diagram to open the workspace
4️⃣ Drag Table Object to create entities
5️⃣ Define attributes for each entity
6️⃣ Use Place Relationship Tool to establish relationships
Example: Members Table Attributes
| Attribute Name | Data Type | Description |
| Membership Number | INT | Unique ID for members |
| Full Name | VARCHAR | Member’s full name |
| Gender | VARCHAR | Male / Female |
| Date of Birth | DATE | DOB of the member |
| Physical Address | VARCHAR | Residential address |
👉Final ER Diagram for MyFlix Video Library
ER Modeling in DBMS: After completing the steps, the ER Diagram should look like this:
Entities and Relationships:
Members (One-to-Many) Movie Rentals (Many-to-One) Movies
Movies (One-to-Many) Categories
Members (One-to-Many) Payments
Once the ER Model is ready, it can be converted into a relational schema for implementation in a database.
👉Summary of ER Modeling in DBMS
🔹 ER Modeling is used for database design and visualization
🔹 Entities represent real-world objects
🔹 Attributes define entity properties
🔹 Relationships connect entities
🔹 EER Model extends ER by supporting specialization, generalization, and aggregation
🔹 ER Diagrams can be easily created using MySQL Workbench
By using ER modeling, businesses can avoid poor database designs, minimize redundancy, and improve data consistency!
