👉Comprehensive Guide to Types of Unit Testing:
- Unit Testing is the foundation of reliable software, ensuring that individual components work as expected.
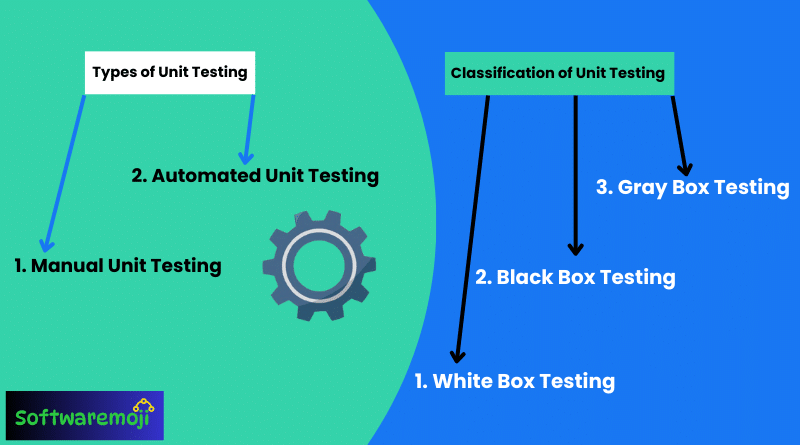
- There are different types of Unit Testing, such as Manual Unit Testing and Automated Unit Testing, to suit various development needs.
- Automated Unit Testing saves time and increases accuracy by running tests with tools like JUnit, NUnit, and PyTest.
- Manual Unit Testing helps developers deeply understand the code logic by testing modules step-by-step without automation.
Comprehensive Guide to Types of Unit Testing: Manual, Automated & Testing Strategies:
👉Introduction:
Unit Testing is a crucial practice in software development, ensuring the reliability and functionality of code. It is categorized based on test execution methods and test strategies. Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the right approach for robust software testing.
👉Types of Unit Testing:
Unit testing can be broadly classified into two primary types based on test execution methods:
👉1. Manual Unit Testing:
Manual unit testing involves testers writing and executing test cases without automation tools. This hands-on approach allows for deeper insights but can be time-consuming.
👉Advantages of Manual Unit Testing:
- High accuracy in scenarios requiring human intuition and understanding.
- Enables exploratory testing beyond scripted test cases.
- Flexible for complex test cases requiring deep comprehension.
- No need for specialized automation tools, making it accessible for small teams.
👉Disadvantages of Manual Unit Testing:
- Slower than automated testing, making it inefficient for large-scale projects.
- Prone to human errors, leading to inconsistent results.
- Resource-intensive, requiring continuous tester involvement.
👉2. Automated Unit Testing:
Automated unit testing uses software tools to execute test cases, making it essential for modern software development.
👉Advantages of Automated Unit Testing:
- Faster execution and repetition, ideal for large projects.
- Eliminates human errors, ensuring consistent results.
- Detects defects more efficiently in integration testing.
- Seamlessly integrates with development methodologies like TDD and CI/CD.
- Saves time and resources in the long run.
👉Disadvantages of Automated Unit Testing:
- High initial setup costs for test scripts and frameworks.
- Requires maintenance as software evolves.
- Less flexible for exploratory and ad-hoc testing.
👉Classification of Unit Testing Based on Strategy:
Beyond execution methods, unit testing is categorized based on testing strategies, each with unique applications.
👉1. White Box Testing:
White Box Testing, also known as structural testing, involves evaluating the internal code structure. It requires programming knowledge and is commonly used by developers.
👉Advantages of White Box Testing:
- Ensures all internal operations work correctly.
- Identifies hidden errors and optimizes code performance.
- Helps developers refine code for better scalability.
👉Disadvantages of White Box Testing:
- Time-consuming and complex, requiring in-depth coding knowledge.
- May not effectively identify missing functionalities.
👉2. Black Box Testing:
Black Box Testing evaluates software functionality without examining the internal code structure. It focuses on input-output validation and is widely used in functional testing.
👉Advantages of Black Box Testing:
- Simple to perform, requiring no coding knowledge.
- Effective in testing user interfaces and functional specifications.
- Suitable for testers with diverse skill levels.
👉Disadvantages of Black Box Testing:
- May overlook internal code issues.
- Less effective for back-end and performance testing.
👉3. Gray Box Testing:
Gray Box Testing combines White Box and Black Box techniques, offering a balanced approach. Testers have partial knowledge of the internal code structure while focusing on external functionality.
👉Advantages of Gray Box Testing:
- Combines the benefits of both White Box and Black Box testing.
- Helps design more effective test cases.
- Useful in security, system integration, and web application testing.
👉Disadvantages of Gray Box Testing:
- Requires a balance of high-level and technical knowledge.
- May not be as deep as White Box Testing in detecting code-level bugs.
Previous Post: QA Testing 2025 :-
👉Conclusion:
Unit testing plays a vital role in software quality assurance. Choosing between manual and automated testing depends on project needs, while selecting the right testing strategy (White, Black, or Gray Box) enhances software reliability. A well-balanced approach ensures efficient, scalable, and high-quality software development.
